In the constantly changing landscape of real estate development, the concept of Right to Light has emerged as a critical consideration for architects, builders, and urban planners alike. Comprehending what a Right to Light survey entails is essential for everyone involved in building projects, particularly in high-density urban environments. This article delves into the significance of Right to Light surveys, investigating their role in protecting the interests of both developers and neighboring properties, while also examining successful case studies that showcase best practices and outcomes.
As we work through the complexities of property development, the implications of Right to Light extend far beyond simple legalities. They play a crucial role in zoning approvals, influencing design choices and project viability. With growing urban density and a push for new constructions, the importance of conducting comprehensive Right to Light assessments cannot be overstated. In https://yamcode.com/ , we will reveal the background and legal basis of Right to Light in the UK, discuss the survey process, and reveal how proactive measures can aid avoid litigation, ultimately fostering harmonious relationships within the community.
Grasping Right to Light
Right to light is a doctrine that permits property owners to enjoy natural light in their buildings from designated windows. This right is established under common law and pertains to properties that have received light through specific openings for a uninterrupted period, typically more than 20 years. The principle seeks to protect the enjoyment of light as a significant aspect of residential and commercial environments, ensuring that developments do not unduly obstruct light access to neighboring properties.
Understanding the relevance of right to light is essential for property developers, as it can significantly impact zoning approvals and project feasibility. If a planned development infringes on a neighboring property's right to light, it can result in complaints, delays in the planning process, and potentially costly legal disputes. Developers must take into account these rights early in the planning phase to avoid complications that might arise later or even halt the project altogether.
Additionally, the implications of right to light go beyond mere access to sunlight; they affect design choices, community relations, and future property values. As urban areas become more crowded and competition for development space intensifies, awareness and attention of right to light issues will become increasingly crucial. Engaging in a right to light assessment can help reveal potential risks and guide developers in developing solutions that satisfy legal requirements while also considering the concerns of neighboring properties.
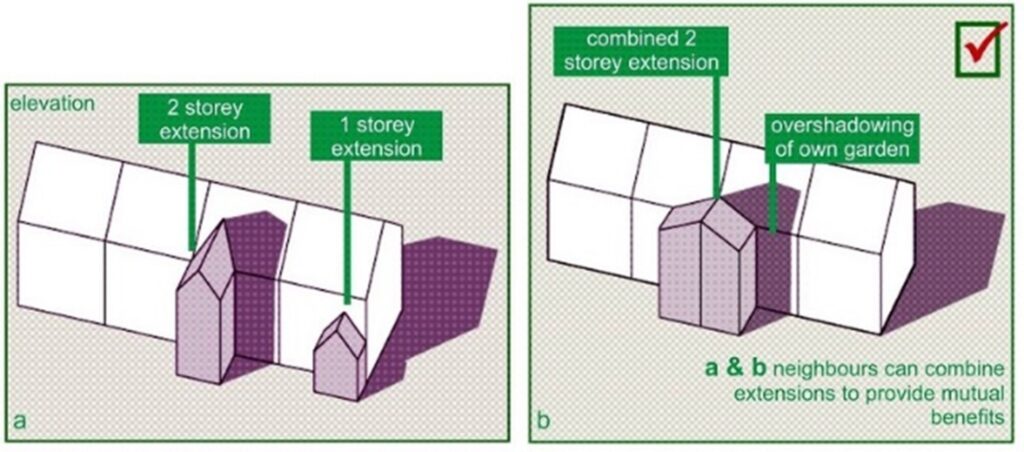
Assessment Process and Techniques
Light Access surveys are crucial for determining potential light blockages and confirming compliance with legal guidelines. The survey procedure starts with site analysis, where surveyors examine the existing light situations and topography around the property. This assessment usually includes calculating sunlight exposure at various intervals of the daily cycle and noting any barriers that may hinder light access to neighboring properties. Collecting both qualitative and quantitative data during this phase is essential for an accurate evaluation.
After the initial data is collected, surveyors employ specialized tools and techniques to assess the effect of any proposed developments on light access. Specialized software is commonly used to create comprehensive 3D models, which simulate how light meets with the structures in question. These models enable surveyors to clearly demonstrate potential infringements on light rights and provide a thorough analysis. The application of BRE guidelines ensures the survey meets industry standards for daylighting assessments.
The result of the assessment procedure is typically a Daylight and Sunlight report, which synthesizes the findings and provides recommendations for mitigating any identified concerns. This report not only assists the developer in obtaining planning approval but also serves as a proactive approach to avoid conflicts with adjacent property owners. By clarifying Right To Light London of right to light in the context of the development, both developers and property owners can maneuver the complexities of city planning with assurance.
Examples and Real-World Insights
In analyzing successful outcomes of right to light surveys, one notable case included a developer in a crowded London neighborhood. At first, confronting objections from neighboring homeowners concerned about reduced daylight due to a planned high-rise, the builder commissioned a thorough right to light survey. The results showed potential infringements and permitted a redesign that took into account the neighbors' concerns, ultimately leading to a successful planning application that harmonized both development goals and light rights.
Another instance comes from a project involving historic buildings in a city center. The developer had ambitions to convert an existing structure into luxury apartments but faced resistance from adjacent property owners claiming rights to light were being compromised. By engaging a right to light expert early in the process, the builder utilized 3D modeling and adhered to BRE guidelines to demonstrate that light levels for neighbors would remain compliant. This proactive approach not only facilitated smoother negotiations but also showcased the importance of integrating right to light assessments in the early stages of development.
In a other case, a residential extension sparked a dispute when neighbors objected, alleging that the new structure would block significant sunlight. The homeowner opted for a right to light survey which revealed the degree of potential impact. Armed with concrete data, the homeowner engaged in constructive discussions with their neighbors to reach an amicable compromise that altered the design of the extension while preserving light access. This case highlights how effective communication and well-informed strategies can reduce conflicts and align interests in right to light matters.
